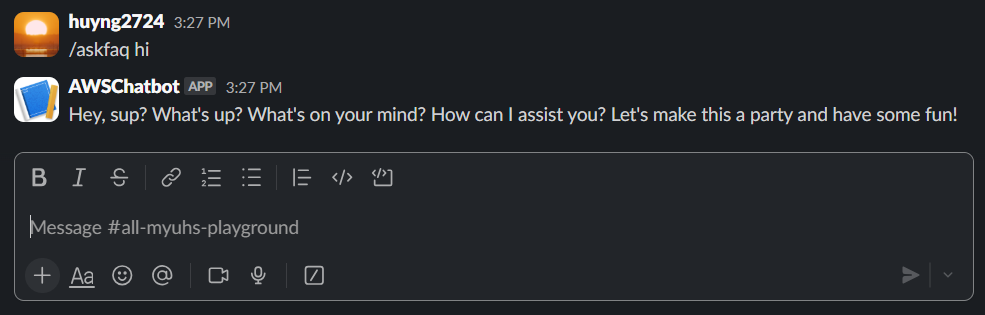
5. Send Response
In this step, we will create an async AWS Lambda function to receive output from the previous Lambda (via API Gateway or event) and send it directly to Slack using the Slack API.
Step 1: Create Lambda function
- Create a Lambda function named
WrapOutput- Runtime: Python 3.x
- Role:
LambdaChatbotExecutionRole - Copy and paste the code below, replacing SLACK_BOT_TOKEN (from Install App) and SLACK_CHANNEL_ID (Go to the Slack channel you want to send messages to. Click the channel name at the top, View channel details. The ID is at the end of the URL or in the channel info) with your actual values:
import json
import urllib.request
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN = "xoxb-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" # Replace with your Slack Bot Token
SLACK_CHANNEL_ID = "C1234567890" # Replace with your Slack Channel ID
def lambda_handler(event, context):
try:
# Receive message from NLPHandler
message = event.get("message", "No message provided")
# Create payload for Slack
payload = {
"channel": SLACK_CHANNEL_ID,
"text": message
}
# Send directly to Slack API
req = urllib.request.Request(
"https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage",
data=json.dumps(payload).encode("utf-8"),
headers={
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Bearer {SLACK_BOT_TOKEN}"
}
)
with urllib.request.urlopen(req) as resp:
slack_response = json.loads(resp.read().decode())
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps({
"status": "Message sent to Slack successfully!",
"slack_response": slack_response
})
}
except Exception as e:
print("=== ERROR in WrapOutput ===")
print(f"[SLACK] Error: {str(e)}")
print(f"[SLACK] Event received: {json.dumps(event, indent=2)}")
return {
"statusCode": 500,
"body": json.dumps({"error": str(e)})
}
Step 2: Check the output message
After completing this, you have finished building a simple messaging flow using Lex and enhanced natural language.